Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -MgAgSb
-MgAgSbLi, J.*; Li, X.*; Zhang, Y.*; Zhu, J.*; Zhao, E.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Avdeev, M.*; Liu, P.-F.*; Sui, J.*; et al.
Applied Physics Reviews (Internet), 11(1), p.011406_1 - 011406_8, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Physics, Applied)Nakayama, Katsumasa*; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review Research (Internet), 5(2), p.L022054_1 - L022054_6, 2023/06
The Casimir effect is a fundamental quantum phenomenon induced by the zero-point energy for a quantum field. It is well-known for relativistic fields with a linear dispersion relation, while its existence or absence for nonrelativistic fields with a quadratic dispersion is an unsettled question. Here, we investigate the Casimir effects for various dispersion relations on the lattice. We find that Casimir effects for dispersions proportional to an even power of momentum are absent in a long distance under some types of boundary conditions, while a remnant of the Casimir effect survives in a short distance. The concepts of such absence and remnants of Casimir effect help us to understand observables in finite-size materials with quantum fields on the lattice, such as thin films, narrow nanoribbons, and short nanowires. In terms of this effect, we also give a reinterpretation of the Casimir effect for massive fields.

Chen, L.*; Mao, C.*; Chung, J.-H.*; Stone, M. B.*; Kolesnikov, A. I.*; Wang, X.*; Murai, Naoki; Gao, B.*; Delaire, O.*; Dai, P.*
Nature Communications (Internet), 13, p.4037_1 - 4037_7, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:53.42(Multidisciplinary Sciences) -type PbS
-type PbSRathore, E.*; Juneja, R.*; Sarkar, D.*; Roychowdhury, S.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Singh, A. K.*; Biswas, K.*
Materials Today Energy (Internet), 24, p.100953_1 - 100953_9, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:85.62(Chemistry, Physical)Wu, P.*; Fan, F.-R.*; Hagihara, Masato*; Kofu, Maiko; Peng, K.*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Lee, S.*; Honda, Takashi*; Yonemura, Masao*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; et al.
New Journal of Physics (Internet), 22(8), p.083083_1 - 083083_9, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:58.58(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Thermoelectric material SnSe has aroused world-wide interests in the past years, and its inherent strong lattice anharmonicity is regarded as a crucial factor for its outstanding thermoelectric performance. However, the understanding of lattice anharmonicity in SnSe system remains inadequate, especially regarding how phonon dynamics are affected by this behavior. In this work, we present a comprehensive study of lattice dynamics on Na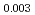 Sn
Sn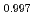 Se
Se S
S by means of neutron total scattering, inelastic neutron scattering, Raman spectroscopy as well as frozen-phonon calculations. Lattice anharmonicity is evidenced by pair distribution function, inelastic neutron scattering and Raman measurements. By separating the effects of thermal expansion and multi-phonon scattering, we found that the latter is very significant in high-energy optical phonon modes. The strong temperature-dependence of these phonon modes indicate the anharmonicity in this system. Moreover, our data reveals that the linewidths of high-energy optical phonons become broadened with mild doping of sulfur. Our studies suggest that the thermoelectric performance of SnSe could be further enhanced by reducing the contributions of high-energy optical phonon modes to the lattice thermal conductivity via phonon engineering.
by means of neutron total scattering, inelastic neutron scattering, Raman spectroscopy as well as frozen-phonon calculations. Lattice anharmonicity is evidenced by pair distribution function, inelastic neutron scattering and Raman measurements. By separating the effects of thermal expansion and multi-phonon scattering, we found that the latter is very significant in high-energy optical phonon modes. The strong temperature-dependence of these phonon modes indicate the anharmonicity in this system. Moreover, our data reveals that the linewidths of high-energy optical phonons become broadened with mild doping of sulfur. Our studies suggest that the thermoelectric performance of SnSe could be further enhanced by reducing the contributions of high-energy optical phonon modes to the lattice thermal conductivity via phonon engineering.
 Ir
Ir Sn
Sn
Kaneko, Koji; Cheung, Y. W.*; Hu, Y.*; Imai, Masaki*; Tanioku, Yasuaki*; Kanagawa, Hibiki*; Murakawa, Joichi*; Moriyama, Kodai*; Zhang, W.*; Lai, K. T.*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 30, p.011032_1 - 011032_6, 2020/03
Murai, Naoki; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Nakajima, Masamichi*; Kawamura, Mitsuaki*; Ishikawa, Daisuke*; Tajima, Setsuko*; Baron, A. Q. R.*
Physical Review B, 101(3), p.035126_1 - 035126_6, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:33.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We report an inelastic X-ray scattering investigation of phonons in FeSe superconductor. Comparing the experimental phonon dispersion with density functional theory (DFT) calculations in the non-magnetic state, we found a significant disagreement between them. A better overall agreement was obtained by allowing for spin-polarization in DFT calculations, despite the absence of magnetic order in FeSe. This calculation gives a realistic approximation, at DFT level, of the disordered paramagnetic state of FeSe, in which strong spin fluctuations are present.
 Sr
Sr )
) Rh
Rh Sn
Sn from a lattice dynamics study
from a lattice dynamics studyCheung, Y. W.*; Hu, Y. J.*; Imai, Masaki*; Tanioku, Yasuaki*; Kanagawa, Hibiki*; Murakawa, Joichi*; Moriyama, Kodai*; Zhang, W.*; Lai, K. T.*; Yoshimura, Kazuyoshi*; et al.
Physical Review B, 98(16), p.161103_1 - 161103_5, 2018/10
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:67.24(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Se
Se
Lee, C. H.*; Nishida, Atsuhiro*; Hasegawa, Takumi*; Nishiate, Hirotaka*; Kunioka, Haruno*; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Nakajima, Kenji; Mizuguchi, Yoshikazu*
Applied Physics Letters, 112(2), p.023903_1 - 023903_4, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:77.9(Physics, Applied)Low energy phonons in LaOBiS Se
Se are studied using inelastic neutron scattering. Dispersionless flat phonon branches that are mainly associated with a large vibration of Bi atoms are observed at a relatively low energy of
are studied using inelastic neutron scattering. Dispersionless flat phonon branches that are mainly associated with a large vibration of Bi atoms are observed at a relatively low energy of  = 6 - 6.7 meV. The phonon energy softens upon Se doping owing to its heavier atomic mass than S atom and the expansion of lattice constant. Simultaneously, the lattice thermal conductivity lowered upon Se doping as the same manner of the phonon softening. These suggest that despite the lack of an oversized cage in LaOBiS
= 6 - 6.7 meV. The phonon energy softens upon Se doping owing to its heavier atomic mass than S atom and the expansion of lattice constant. Simultaneously, the lattice thermal conductivity lowered upon Se doping as the same manner of the phonon softening. These suggest that despite the lack of an oversized cage in LaOBiS Se
Se , rattling motions of Bi atoms can scatter phonon like rattling in cage compounds, contributing to enhance the thermoelectric property.
, rattling motions of Bi atoms can scatter phonon like rattling in cage compounds, contributing to enhance the thermoelectric property.
Kai, Takeshi; Yokoya, Akinari; Ukai, Masatoshi*; Watanabe, Ritsuko
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 108, p.13 - 17, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:89.99(Chemistry, Physical)Role of secondary electrons on DNA damage have not been understood sufficiently because there still exists a lack of cross section of rotational and phonon excitation in the liquid phase for precise simulation of the electron behavior. We calculated cross sections, stopping powers, and energy loss rates for the excitations in liquid water. The values for rotation are less by three orders of magnitude than those in the gas phase, while the values for phonon are close to those reported for amorphous ice. Thermalization process has so far been estimated from an assumption that the energy loss rates do not depend strongly on the energy below 1 eV. However, we found that the energy loss rates depend significantly on the energy. This fact indicates that the thermalization time will be longer than the previously estimated time, and we predict that thermalization process strongly involve in subsequent hydrated and chemical processes. The data set provide here is expected to useful to make the role of the secondary electrons on DNA damage much clear.

Metoki, Naoto; Kaneko, Koji; Raymond, S.*; Sanchez, J. P.*; Piekarz, P.*; Parlinski, K.*; Ole , A. M.*; Ikeda, Shugo; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Haga, Yoshinori; et al.
, A. M.*; Ikeda, Shugo; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Haga, Yoshinori; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 378-380, p.1003 - 1004, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:49.71(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
 superconductivity
superconductivityTachiki, Masashi*; Machida, Masahiko; Egami, Takeshi*
Physical Review B, 67(17), p.174506_1 - 174506_12, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:47 Percentile:85.25(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Fukuda, Tatsuo
Hamon, 13(1), p.43 - 46, 2003/01
no abstracts in English
 -graphite intercalation compounds
-graphite intercalation compounds*; Mitsui, Takaya; Harami, Taikan; Yoda, Yoshitaka*; *
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 38(SUPPL.38-1), p.535 - 537, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
 LA phonon of CuGeO
LA phonon of CuGeO
Nishi, Masakazu*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa*; Fujii, Yasuhiko*; Katano, Susumu; Akimitsu, Jun*; M.Yethiraj*; Fernandez-Baca, J. A.*
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 60(8-9), p.1109 - 1111, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:33.75(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 phonon dispersion relation of the
phonon dispersion relation of the 
 -phases in Ni-Co-Al alloys
-phases in Ni-Co-Al alloys*; *; *; Morii, Yukio
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 60(8-9), p.1427 - 1429, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Katagiri, Masaki; Kishimoto, Maki; Ukibe, M.*; Nakamura, Tatsuya*; Kurakado, M.*; Maehata, Keisuke*; *; Nakazawa, Masaharu*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 37(SUPPL.37-2), p.13 - 18, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:36.37(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
 P
P Se
Se studied by means of neutron scattering
studied by means of neutron scatteringS.W.H.Eijt*; R.Currat*; J.E.Lorenzo*; P.Gregoire*; Katano, Susumu; T.Janssen*; B.Hennion*; Y.Vysochanskii*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 10(22), p.4811 - 4844, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:88.63(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
Ishii, Yoshinobu; *; Onodera, Akifumi*; *; Morii, Yukio
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 241-243, p.409 - 411, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27.12(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
Saito, Tamotsu; K.Deng*; Nakano, Junichi; Yamada, Reiji
JAERI-Research 97-001, 18 Pages, 1997/01
no abstracts in English